Now in Measurement Science and Technology!
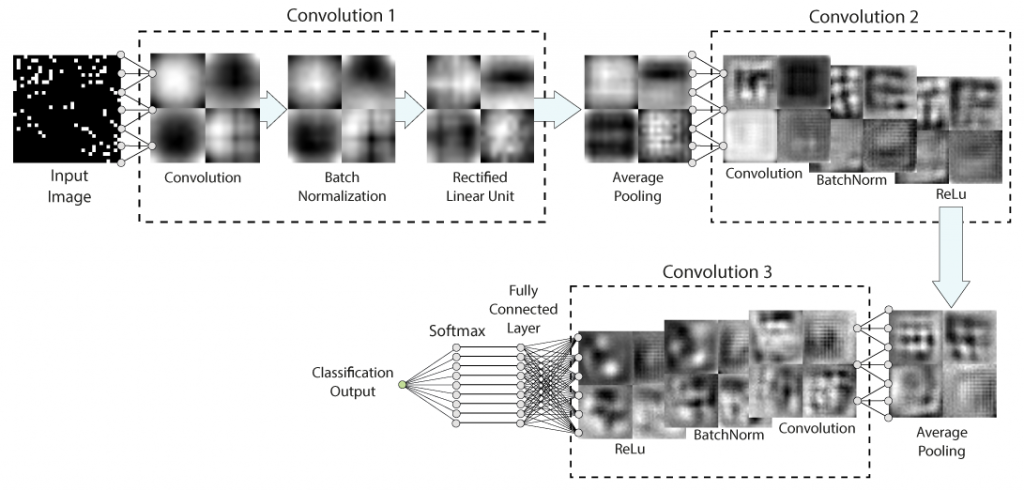
In collaboration with our theory colleague at IQOQI (Rick van Bijnen) we present a novel method for the analysis of quantum gas microscope images. Our method uses deep learning to improve the fidelity with which lattice sites can be classified as occupied or unoccupied. This method is able to improve upon the fidelity of threshold-based methods, following training on large data sets of simulated images.
We demonstrate the effectiveness of the neural networks especially for the analysis of noncooled lattice images, as it is planned for our future Erbium quantum gas microscope. Here, low photon counts and atom movement limits the fidelity of traditional reconstruction techniques.
