Welcome Alex!
 FF
FF
Emergence of chaotic scattering in ultracold Er and Dy
ERBIUM NEWS:
Now in PRX! We show that for ultracold magnetic lanthanide atoms (Er and Dy) chaotic scattering emerges due to a combination of anisotropic interaction potentials and Zeeman coupling under an external magnetic field. The scattering is studied in a collaborative experimental and theoretical effort, involving our group, the Stuttgart Dy Group led by T. Pfau and the theory colleagues S. Kotochigova and E. Tiesinga in the USA. [more]
Ultracold polar molecules composed of strongly magnetic atoms
ERBIUM NEWS
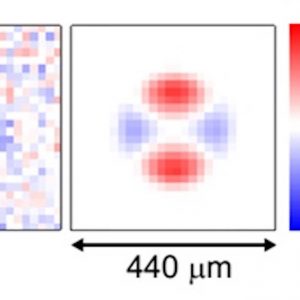
Now in PRL! We created a novel type of dipolar system made of two ultracold bosonic dipolar atoms bounded into a molecules. This work is the result of a combined experimental and theoretical effort between our group, the cold collisions group at LAC in France, and the theory group at Temple University (USA). [more]
Anisotropic Relaxation Dynamics in a Dipolar Fermi Gas Driven Out of Equilibrium
ERBIUM NEWS
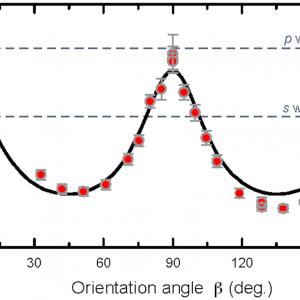
We report on the observation of a large anisotropy in the rethermalization dynamics of an ultracold dipolar Fermi gas driven out of equilibrium. Our system consists of an ultracold sample of strongly magnetic Er167 fermions, spin polarized in the lowest Zeeman sublevel. In this system, elastic collisions arise purely from universal dipolar scattering. Based on cross-dimensional rethermalization experiments, we observe a strong anisotropy of the scattering, which manifests itself in a large angular dependence of the thermal relaxation dynamics. Our result is in good agreement with recent theoretical predictions. Furthermore, we measure the rethermalization rate as a function of temperature for different angles and find that the suppression of collisions by Pauli blocking is not influenced by the dipole orientation.[more]
Observation of Fermi surface deformation in a dipolar quantum gas
ERBIUM NEWS
Now in Science! In the presence of isotropic interactions, the Fermi surface of an ultracold Fermi gas is spherical. Introducing anisotropic interactions can deform it. This effect is subtle and challenging to observe experimentally. We report the observation of such a Fermi surface deformation in a degenerate dipolar Fermi gas of erbium atoms. The deformation is caused by the interplay between strong magnetic dipole-dipole interaction and the Pauli exclusion principle. We demonstrate the many-body nature of the effect and its tunability with the Fermi energy. Our observation provides a basis for future studies on anisotropic many-body phenomena in normal and superfluid phases. [more]
Quantum Chaos in Ultracold Collisions of Erbium
ERBIUM NEWS
We have studied the scattering behavior of ultracold Er atoms and observed an enormous number of Fano-Feshbach scattering resonances and demonstrate high correlation in the spectra, underlying chaotic scattering between the particles. This work, now published in NATURE, is a joint effort between our group, John L. Bohn from JILA (Boulder, Colorado), and the team of Svetlana Kotochigova at Temple University (USA). Nice media coverage (in italian) from the MEDIA INAF. [more]